Pathophysiology Of Chronic Kidney Disease Diagram
30 million people in the united states are living with chronic kidney disease ckd. The main causes of renal injury are based on immunologic reactions initiated by immune complexes or immune cells tissue hypoxia and ischaemia exogenic agents like drugs endogenous substances like glucose or paraproteins and others and genetic defects.
 Pathophysiology Of Chronic Renal Failure Condensed Part 1
Pathophysiology Of Chronic Renal Failure Condensed Part 1
Kidney failure or otherwise known as renal failure or kidney injury can be categorized to either acute or chronic kidney failures depending on the severity of the disease condition.
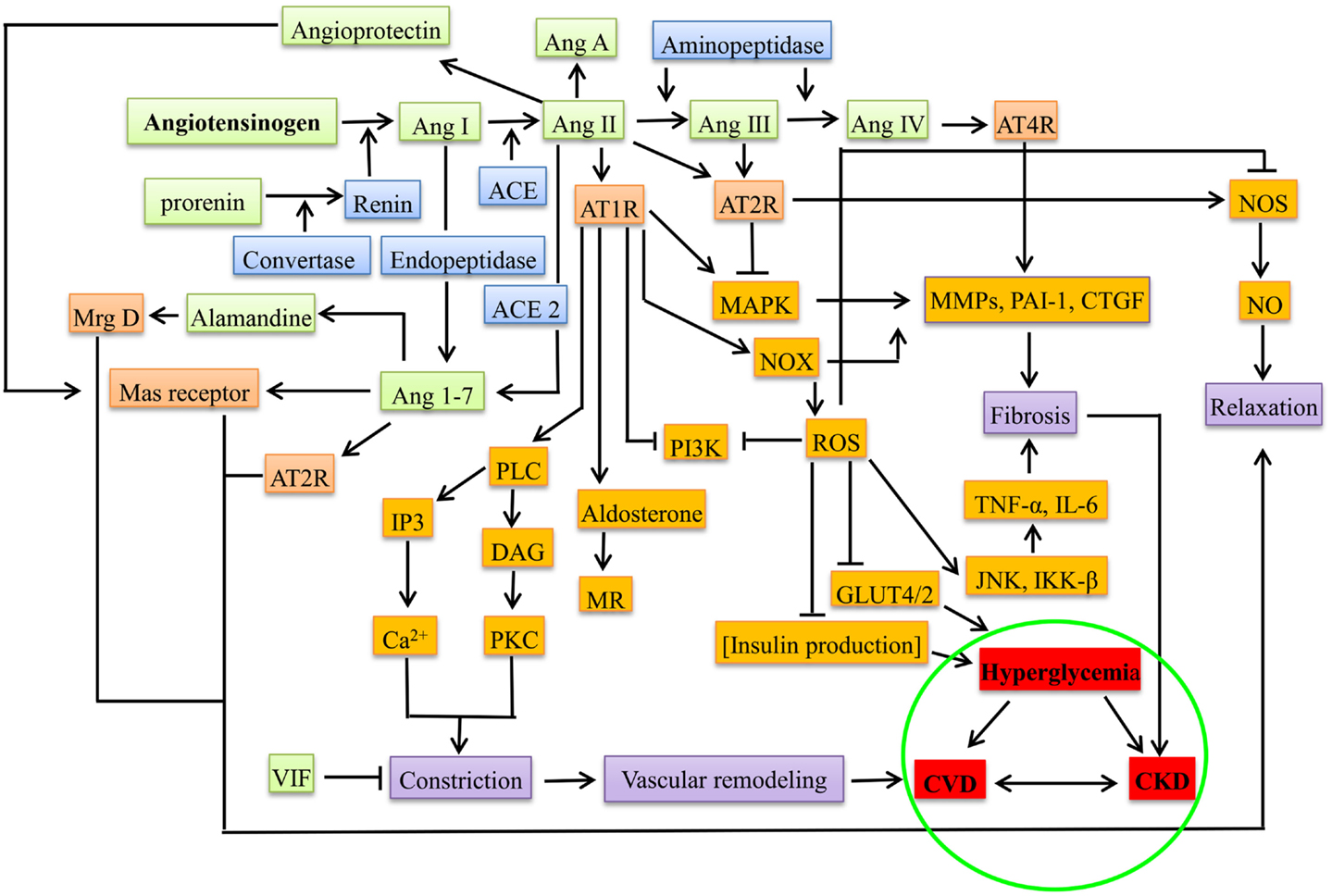
Pathophysiology of chronic kidney disease diagram. Pathologic features include fibrosis loss of renal cells and infiltration of renal tissue by monocytes and macrophages. The rat has classically been the species of choice for pharmacological studies and disease modeling providing a source of high quality physiological data on cardiovascular and renal pathophysiology over many decades. There are many diseases that cause chronic renal disease.
Angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors acei and angiotensin ii receptor blockers arbs block the effects of angiotensin ii on i sodium and fluid retention ii vasoconstriction. 12 pathophysiology of kidney disease. Schematic diagram non modifiable factors hereditary age greater than 60 years old gender race modifiable factors diabetic mellitus hypertension increase protein and cholesterol intake smoking use of analgesics decreased renal blood flow primary kidney disease damage from other diseases.
Acute kidney failure is considered to be the abrupt loss of kidney function while chronic kidney failure is defined as the progressive reduction of renal functioning by which referring to the remaining kidney mass that can no longer sustain the needs of the body. The term chronic kidney disease means lasting damage to the kidneys that can get worse over time. Chronic kidney disease also called chronic kidney failure describes the gradual loss of kidney function.
Regardless of the etiology chronic kidney disease is characterized by renal fibrosis glomerulosclerosis and tubulointerstitial fibrosis. The impairment of the tubulointerstitium tubulointerstitial fibrosis and tubular atrophy is at least as important as that of the glomeruli glomerulosclerosis. Tight blood pressure control.
When chronic kidney disease reaches an advanced stage dangerous levels of fluid electrolytes and wastes can build up in your body. If the damage is very bad your kidneys may stop working. Causes and distribution of chronic kidney disease the incidence of chronic renal failure is approximately 10 cases per 100000 people.
However there are common mechanisms for disease progression. Recent developments in genome engineering now allow us to capitalize on the wealth of knowledge acquired over the last century. Know if you have chronic kidney disease.
Each has its own pathophysiology. Your kidneys filter wastes and excess fluids from your blood which are then excreted in your urine. In industrialized nations alone tens of thousands of people are dependent on dialysis because of the widespread contributory causes of chronic kidney failure in these countries.
Reducing damage due to the end organ effects of hypertension on the kidney as well as the heart.
 Bone Loss In Chronic Kidney Disease Quantity Or Quality
Bone Loss In Chronic Kidney Disease Quantity Or Quality
 Flow Chart Showing The Selection Process Ckd Chronic Kidney
Flow Chart Showing The Selection Process Ckd Chronic Kidney
 Flow Chart Of Cohort Formation Ckd Chronic Kidney Disease Egfr
Flow Chart Of Cohort Formation Ckd Chronic Kidney Disease Egfr
 Management Of Secondary Hyperparathyroidism In Ckd Stages 3 And 4
Management Of Secondary Hyperparathyroidism In Ckd Stages 3 And 4
 Pathogenesis And Treatment Of Chronic Kidney Disease Mineral And
Pathogenesis And Treatment Of Chronic Kidney Disease Mineral And
 Pathophysiology Of Hyperphosphatemia Phosphate Control In Chronic
Pathophysiology Of Hyperphosphatemia Phosphate Control In Chronic
 Chronic Kidney Disease Ckd Mcmaster Pathophysiology Review
Chronic Kidney Disease Ckd Mcmaster Pathophysiology Review
 Cells Free Full Text Autophagy In Chronic Kidney Diseases
Cells Free Full Text Autophagy In Chronic Kidney Diseases
 Peculiarities In The Physical Examination Of The Patients With Renal
Peculiarities In The Physical Examination Of The Patients With Renal
 Chronic Kidney Disease Pathophysiology Schematic Diagram Nursing
Chronic Kidney Disease Pathophysiology Schematic Diagram Nursing
 Pathophysiology Of Chronic Kidney Disease Mineral And Bone Disorder
Pathophysiology Of Chronic Kidney Disease Mineral And Bone Disorder
 Pathogenesis Of Chronic Kidney Disease Tubulointerstitial Hypoxia
Pathogenesis Of Chronic Kidney Disease Tubulointerstitial Hypoxia
 Schematic Diagram Of Interactions Among Chronic Kidney Disease
Schematic Diagram Of Interactions Among Chronic Kidney Disease
 Nephro Urology Monthly Associations Between Hyperuricemia And
Nephro Urology Monthly Associations Between Hyperuricemia And
 Kidney Disease Chronic Renal Failure Healthengine Blog
Kidney Disease Chronic Renal Failure Healthengine Blog
 Frontiers Cellular And Molecular Mechanisms Of Chronic Kidney
Frontiers Cellular And Molecular Mechanisms Of Chronic Kidney
 Acute And Chronic Renal Failure Easy Slides
Acute And Chronic Renal Failure Easy Slides
 Global Dialysis Dialysis World News
Global Dialysis Dialysis World News
 Consensus Document For The Detection And Management Of Chronic
Consensus Document For The Detection And Management Of Chronic
 Figure 1 From Hypertension In Children With Chronic Kidney Disease
Figure 1 From Hypertension In Children With Chronic Kidney Disease
 Chronic Kidney Disease Cognitive Dysfunction In Chronic Kidney
Chronic Kidney Disease Cognitive Dysfunction In Chronic Kidney
 Chronic Kidney Disease Pathophysiology Medical School Nursing
Chronic Kidney Disease Pathophysiology Medical School Nursing
 Smoking A Risk Factor For Progression Of Chronic Kidney Disease And
Smoking A Risk Factor For Progression Of Chronic Kidney Disease And
 Chronic Kidney Disease An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
Chronic Kidney Disease An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
 Chronic Kidney Disease Pathophysiology Schematic Diagram 52k Views
Chronic Kidney Disease Pathophysiology Schematic Diagram 52k Views
 Obesity And Kidney Disease Bjn Brazilian Journal Of Nephrology
Obesity And Kidney Disease Bjn Brazilian Journal Of Nephrology
 Ghrelin And Leptin Pathophysiology In Chronic Kidney Disease
Ghrelin And Leptin Pathophysiology In Chronic Kidney Disease
 Perpetuating Triad Of Chronic Kidney Disease Anaemia And
Perpetuating Triad Of Chronic Kidney Disease Anaemia And



0 Response to "Pathophysiology Of Chronic Kidney Disease Diagram"
Post a Comment