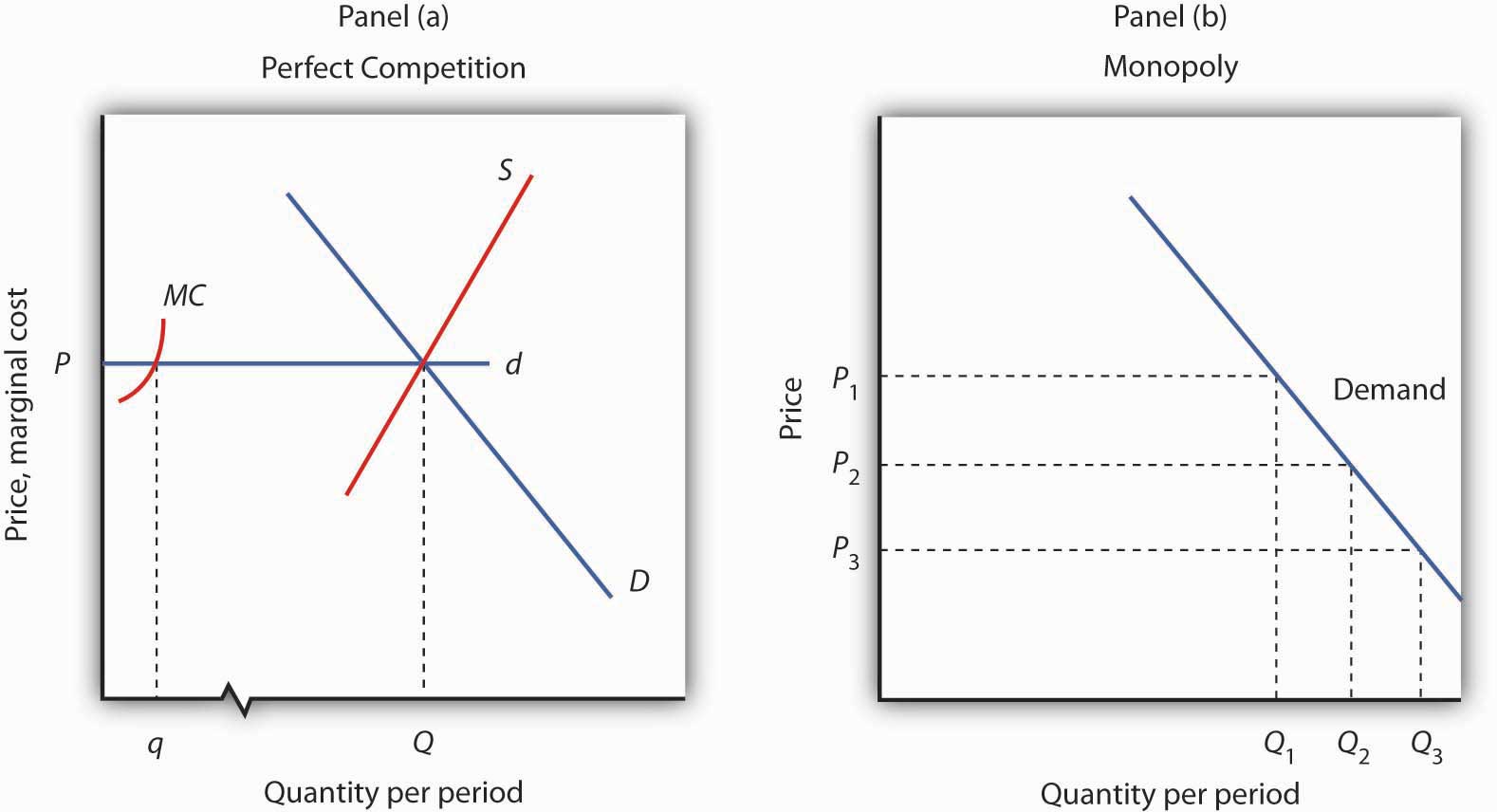
If The Competitive Firm Depicted In This Diagram Produces Output Q It Will
B earn a normal economic profit. So the firms supply curve is exactly the mc curve.
If the competitive firm depicted in this diagram produces output q it will a.
If the competitive firm depicted in this diagram produces output q it will. Earn an economic profit. Achieve productive efficiency but not allocative efficiency. Demand is relatively elastic.
A purely competitive firm is precluded from making economic profits in the long run because. Of unimpeded entry to the industry. 100 point if the competitive firm depicted in this diagram produces output q it will suffer an economic loss.
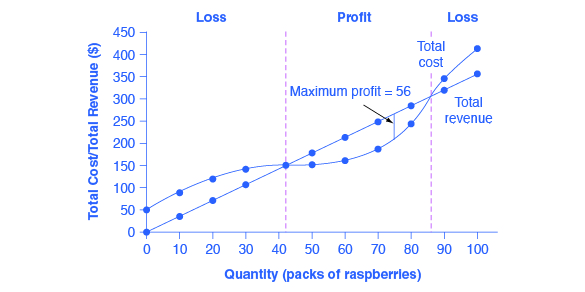
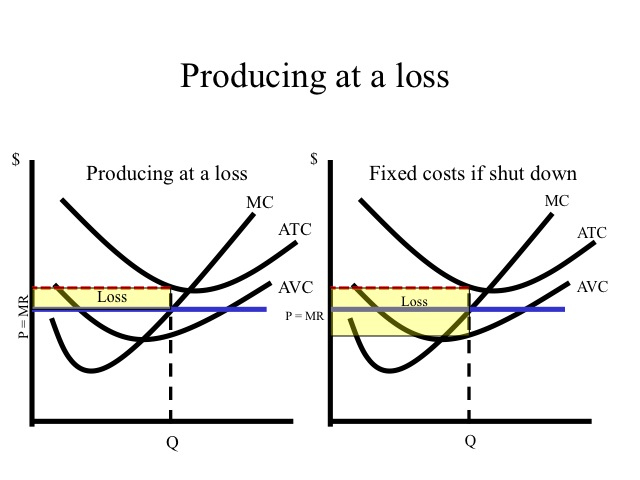
The loss minimizing position of a competitive firm in the short run. Earn a normal profit. Profit increases with output until it reaches a maximum of 150 at q 10 and then decreases as q is increased further.
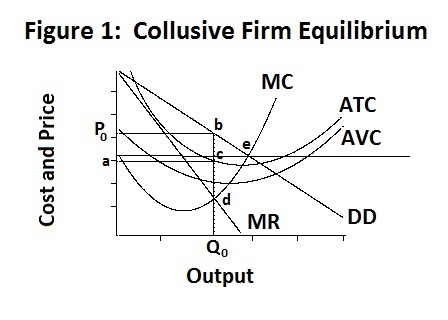
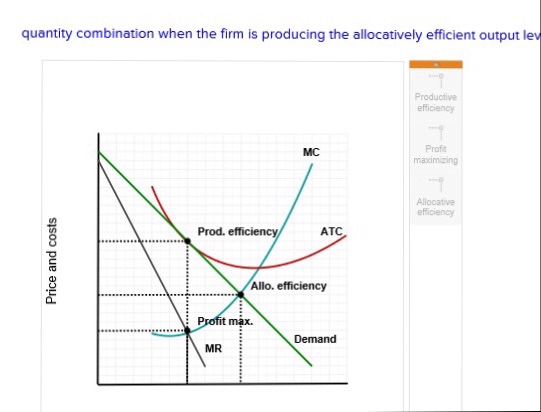
If a firm is in a competitive market and produces at q2 its average costs will be ac2. Achieve productive efficiency but not allocative efficiency. Suffer an economic loss.
Refer to the above diagram. Suppose losses cause industry x to contract and as a result the prices of relevant inputs decline. Earn a normal profit.
A monopoly can increase output to q1 and benefit from lower long run average costs ac1. Refer to the above diagram. Earn a normal profit.
This means it can. D achieve productive efficiency but not allocative efficiency. If this competitive firm produces output q it will.
Earn a normal profit refer to the above diagrams which pertain to a purely competitive firm producing out put q and the industry in which it operates. If this competitive firm produces output q it will. Refer to the above diagram.
If this competitive firm produces output q it will. Tc tr and π are plotted in fig. A suffer an economic loss.
Refer to the above diagram. A competitive firm faces a horizontal demand curve. A firm will produce and sell at an output level where p mc.
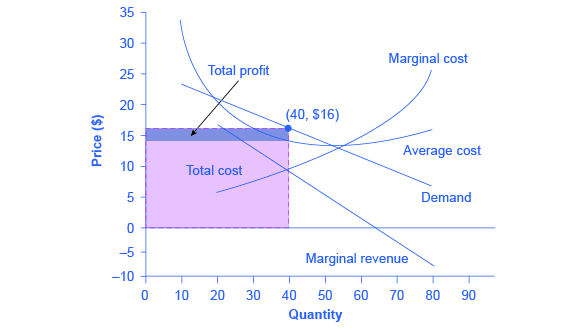
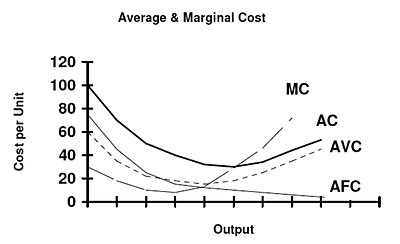
Earn an economic profit. When the firm produces no output or little output profit is negative because of the fixed cost. Competitive firms and markets we have learned the production function and cost function the question.
C earn a positive economic profit. If this competitive firm produces output q it will. In industries with high fixed costs it can be more efficient to have a monopoly than several small firms.
Suffer an economic loss.
 8 2 How Perfectly Competitive Firms Make Output Decisions
8 2 How Perfectly Competitive Firms Make Output Decisions
 Duopoly Cournot Nash Equiibrium
Duopoly Cournot Nash Equiibrium
 Perfect Competition The Shut Down Price Economics Tutor2u
Perfect Competition The Shut Down Price Economics Tutor2u
Business Learning Center Econ 101 Hansen Handout 1 Math
Business Learning Center Econ 101 Hansen Handout 1 Math
 Profit Maximization Under Monopolistic Competition Microeconomics
Profit Maximization Under Monopolistic Competition Microeconomics
 Ch08 Solution To Eight Edition Studocu
Ch08 Solution To Eight Edition Studocu
 Theory Of Production Economics Britannica Com
Theory Of Production Economics Britannica Com
 7 3 Producer Theory In The Long Run Principles Of Microeconomics
7 3 Producer Theory In The Long Run Principles Of Microeconomics
 Profit Maximization In A Perfectly Competitive Market Microeconomics
Profit Maximization In A Perfectly Competitive Market Microeconomics
 Perfect Competition Characteristics Analysis Economics Online
Perfect Competition Characteristics Analysis Economics Online

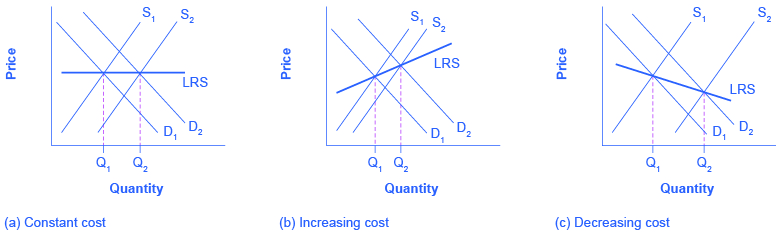 Entry And Exit Decisions In The Long Run Article Khan Academy
Entry And Exit Decisions In The Long Run Article Khan Academy
 Theory Of Production Economics Britannica Com
Theory Of Production Economics Britannica Com
13monopolistic Competition And Oligopoly
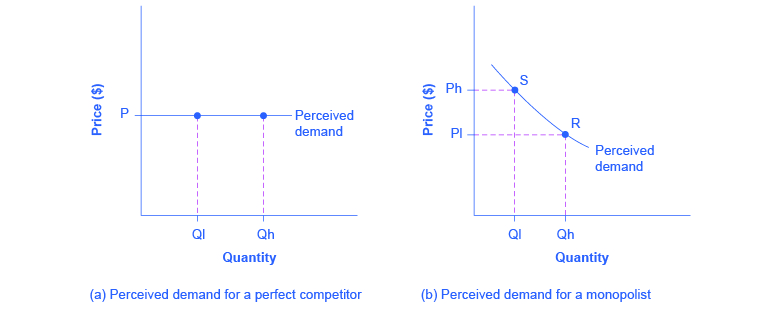 9 2 How A Profit Maximizing Monopoly Chooses Output And Price
9 2 How A Profit Maximizing Monopoly Chooses Output And Price

 8 4 Monopolistic Competition Principles Of Microeconomics
8 4 Monopolistic Competition Principles Of Microeconomics
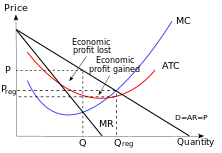
0 Response to "If The Competitive Firm Depicted In This Diagram Produces Output Q It Will"
Post a Comment