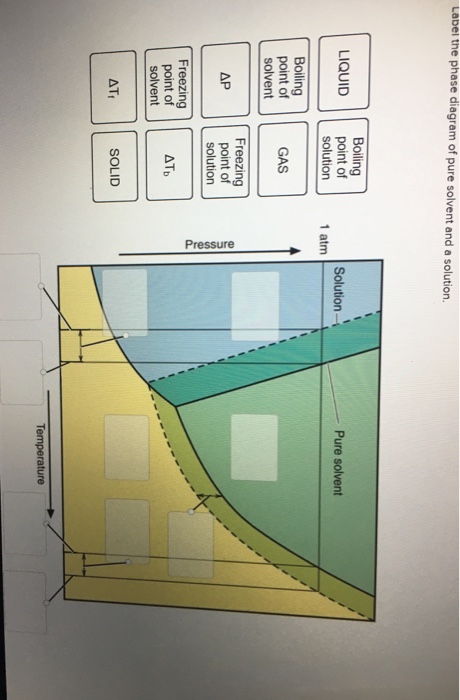
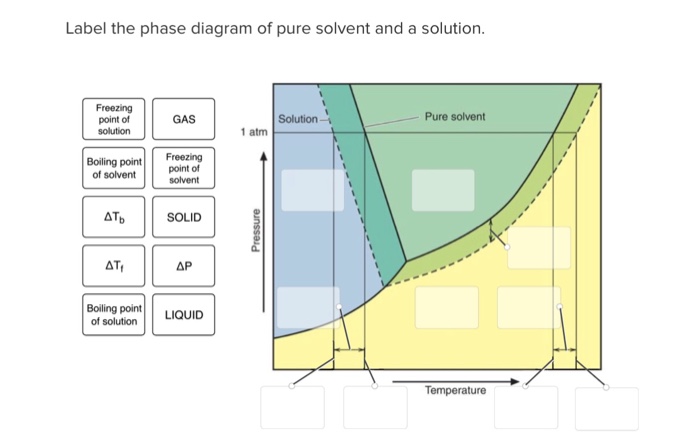
Label The Phase Diagram Of Pure Solvent And A Solution
Pure a and pure b are also considered to be α and β phases respectively. Finally notice that the solid gas curves for the solvent and its solution are identical.
 Diagram Of Solvent Wiring Diagram Gol
Diagram Of Solvent Wiring Diagram Gol
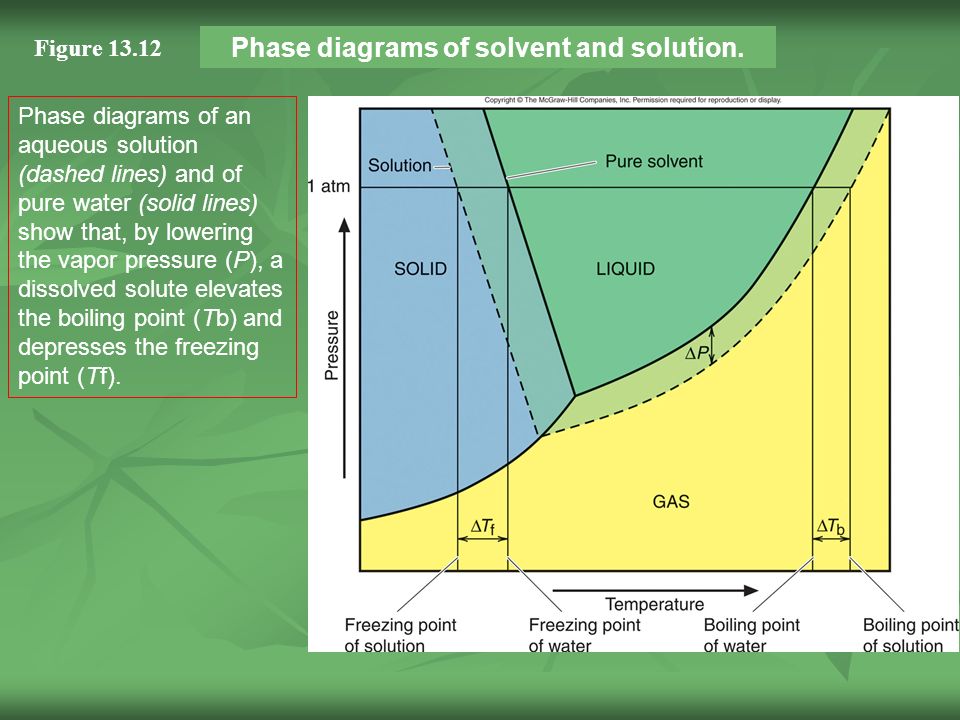
The solid liquid curve for the solution is displaced left of that for the pure solvent representing the freezing point depression δtf that accompanies solution formation.
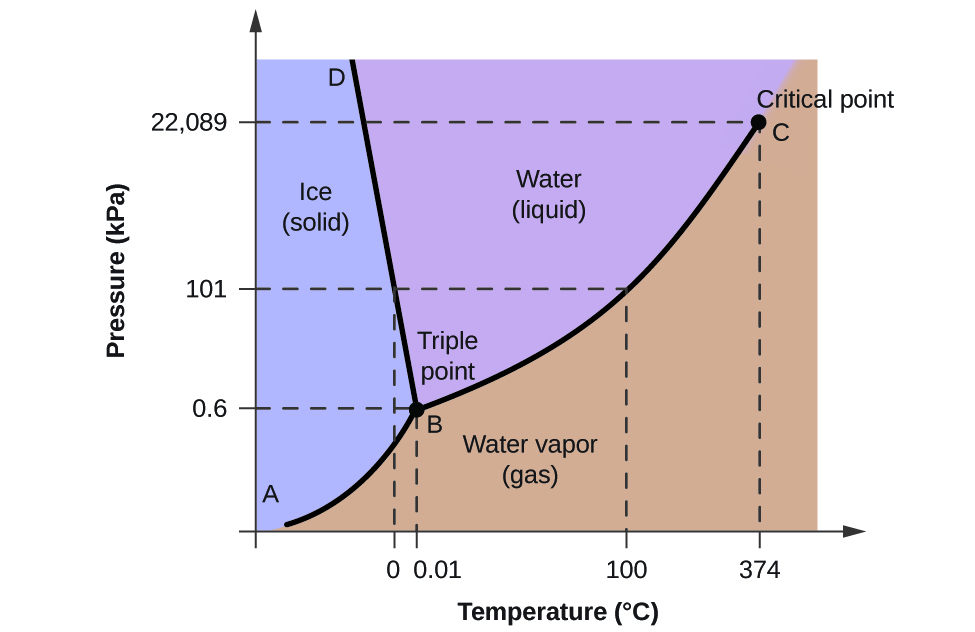
Label the phase diagram of pure solvent and a solution. Introduced to the system forming a homogeneous solution however the phase diagram drastically changes. Phase solid argon must be the denser phase. E the temperature of the substance is increasing.
A pure solvent solution 0 time 0 5 10 15 20 0 time 0 5 10 15 20 b i mass of pure solvent. Label the phase diagram of pure solvent and a solution. Freezing point of pure solvent.
Show transcribed image text. The phase diagrams for a pure solvent and the solvent in a solution are shown. A the molecules are leaving the liquid phase.
Otherwise in β phase solid solution a is the solute. You can think of this as a simple phase diagram. The vaporization curve for the solution lies below the curve for pure water at all temperatures which results in an increase in the boiling point and a decrease in the freezing point of the solution.
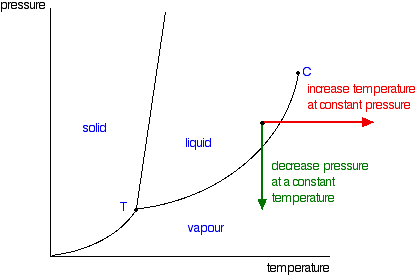
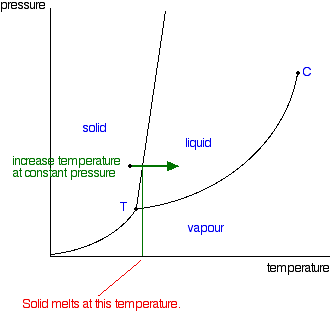
The normal boiling points are the temperature for which vapor pressure equals one atmosphere. If you have a mixture of 100 g of potassium nitrate and 100 g of water and the temperature is above 57c you have a single phase a solution of potassium nitrate. Freezing point of resulting solution ii determine the change in freezing point δt δt kƒ m where m mol solute.
α β and liquid. For example the addition of a solute to a pure solvent making a solution can disrupt important interactions between solvent molecules changing the temperature at which the solvent would typically freeze or boil. Expert answer 100 33 ratings.
Three single phase regions are found on the diagram. A solute reduces the vapor pressure of a solvent at a given temperature so the solution is represented by the blue line. The α phase is a solid solution rich in a atom.
Identify the normal freezing fpsolv and boiling bpsolv points for the pure solvent and the normal freezing fpsoln and boiling bpsoln points of the solution at 1 atm. Mass of unknown solid solute added to pure solvent. This problem has been solved.
It has b atom as the solute component. Assume the solute is nonvolatile and that the solid that freezes from solution is pure solvent. C the vapor pressure of the substance is decreasing.
B the solid and liquid phases coexist in equilibrium. This is the case for many solutions comprising liquid solvents and nonvolatile solutes. D the average intermolecular distance is decreasing.
Phase diagrams of pure water and an aqueous solution of a nonvolatile solute.
 Ternary Phase Diagram An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
Ternary Phase Diagram An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
Introduction To Chemical Engineering Processes Vapor Liquid
 The Properties Of Solutions Ppt Download
The Properties Of Solutions Ppt Download
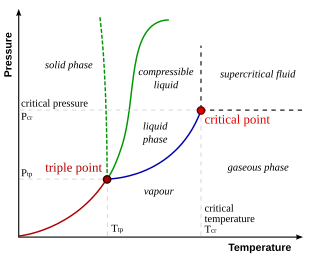
 Phase Diagrams Of Pure Substances
Phase Diagrams Of Pure Substances
 Phase Diagrams Of Pure Substances
Phase Diagrams Of Pure Substances
 Evaporation Filtration And Crystallisation Cpd Education In
Evaporation Filtration And Crystallisation Cpd Education In
 Baseballot Wins Don T Fill Seats But The Marlins Will
Baseballot Wins Don T Fill Seats But The Marlins Will
 Raoult S Law Chemistry Libretexts
Raoult S Law Chemistry Libretexts
 General Chemistry Reading Assignment Solutions Top Hat
General Chemistry Reading Assignment Solutions Top Hat
 Diagram Of Solvent Wiring Diagram Gol
Diagram Of Solvent Wiring Diagram Gol
 Chapter 10 Phase Diagrams Ppt Download
Chapter 10 Phase Diagrams Ppt Download
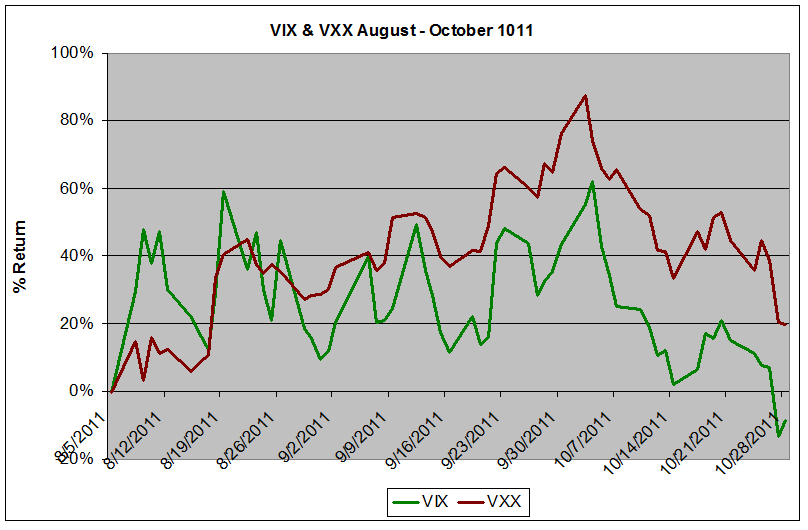 Volatility Surges 35 On Grexit Fears It S Time To Start Shorting
Volatility Surges 35 On Grexit Fears It S Time To Start Shorting
Chapter 46 Pan Tropical Survey Of Forest Cover Changes 1980 2000
 Ternary Phase Diagram An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
Ternary Phase Diagram An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
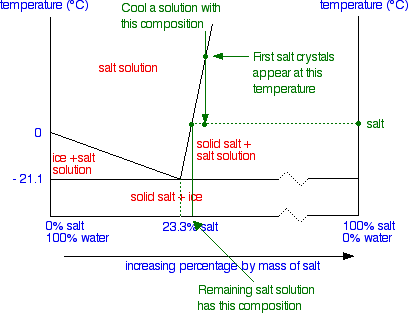 Solid Liquid Phase Diagrams Salt Solution
Solid Liquid Phase Diagrams Salt Solution
Introduction To Chemical Engineering Processes Vapor Liquid
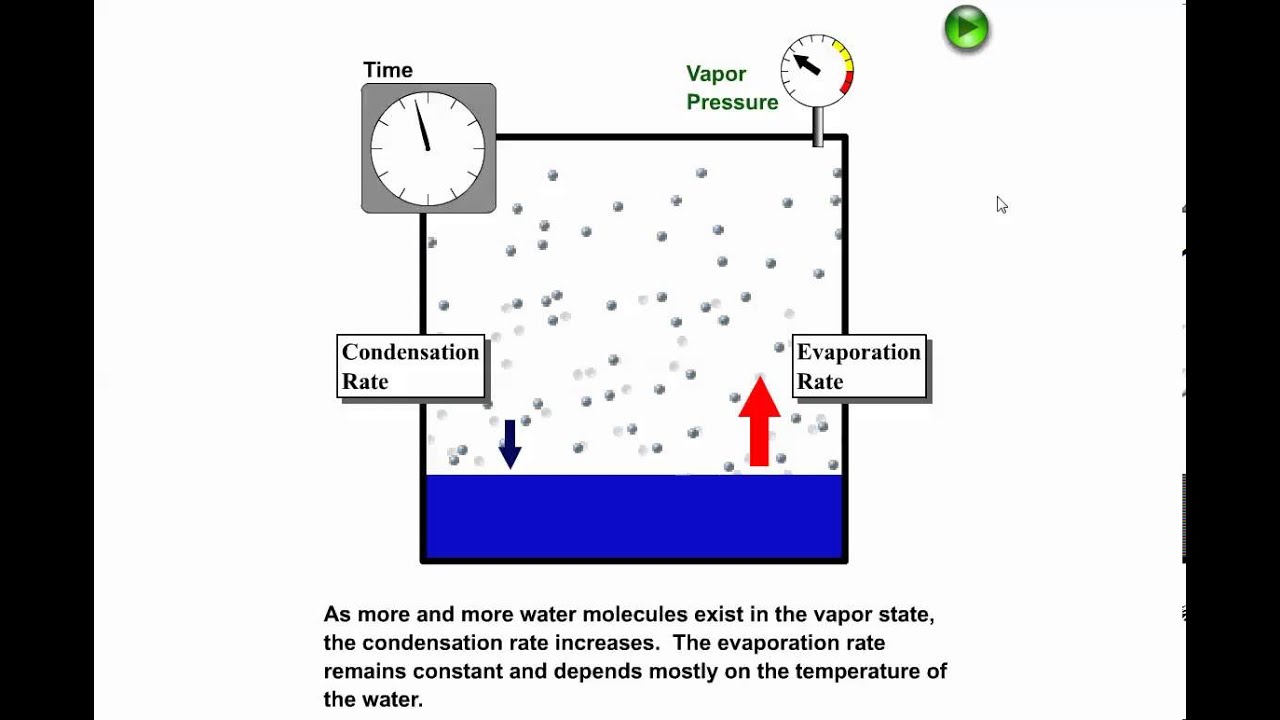 Phase Changes Boundless Chemistry
Phase Changes Boundless Chemistry
 Narrow Equilibrium Window For Complex Coacervation Of Tau And Rna
Narrow Equilibrium Window For Complex Coacervation Of Tau And Rna
Effect Of Solutes On Water Lab Cat
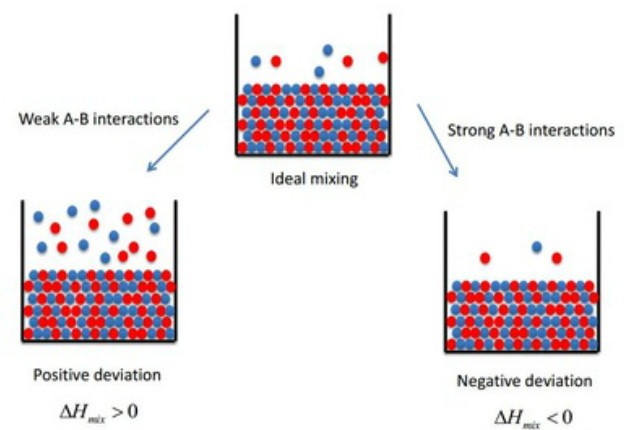 Ideal Non Ideal Solutions Raoult S Law Types Of Solutions
Ideal Non Ideal Solutions Raoult S Law Types Of Solutions

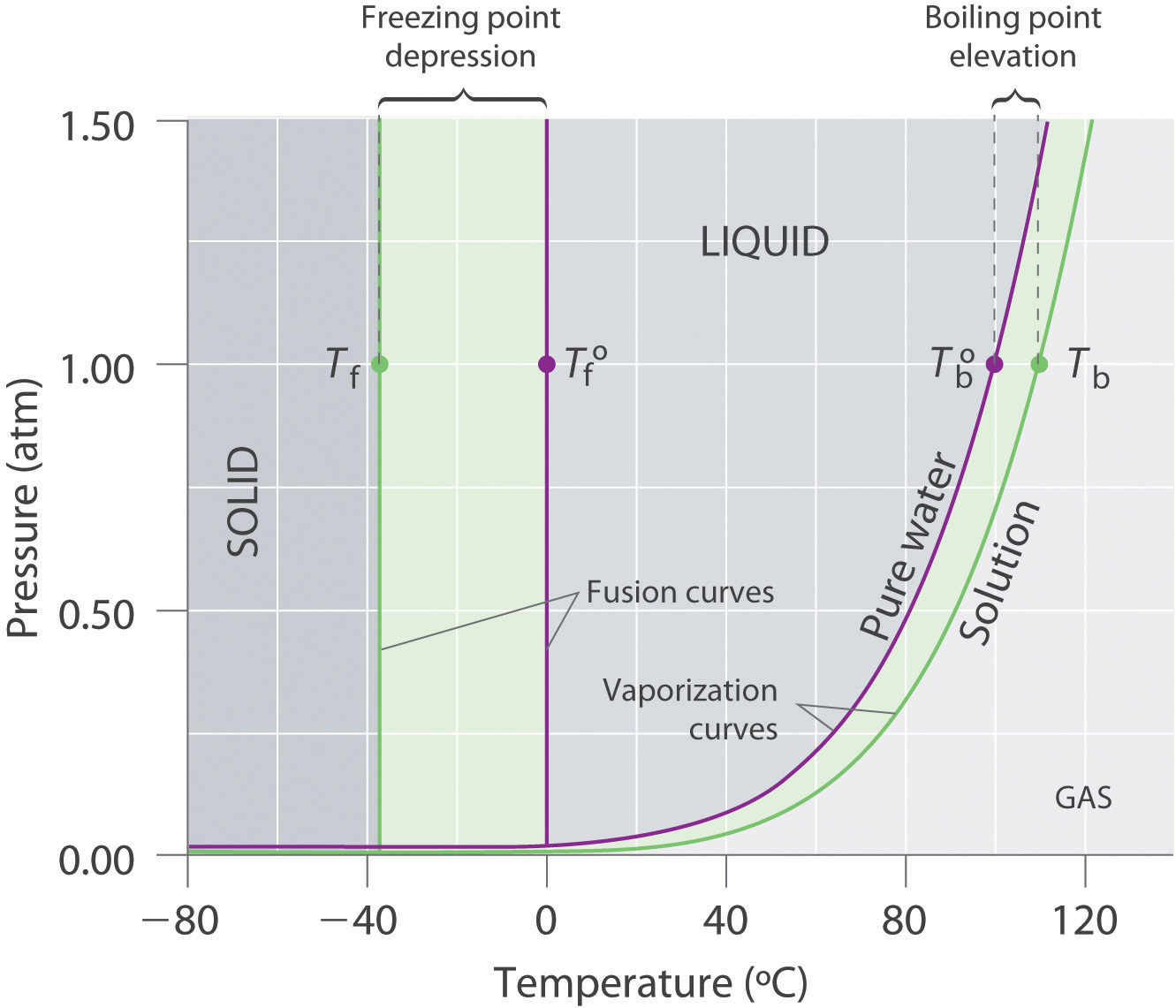
0 Response to "Label The Phase Diagram Of Pure Solvent And A Solution"
Post a Comment