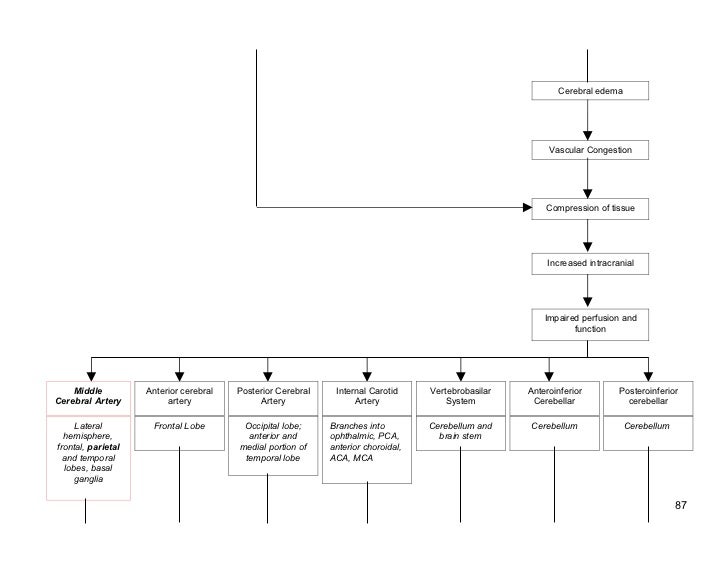
Hemorrhagic Stroke Pathophysiology Diagram
The symptoms are relatively the same as a stroke but last less than 24 hours whereas stroke symptoms persist for greater than 24 hours. Pathophysiology diagram stroke download as word doc doc docx pdf file pdf text file txt or view presentation slides online.
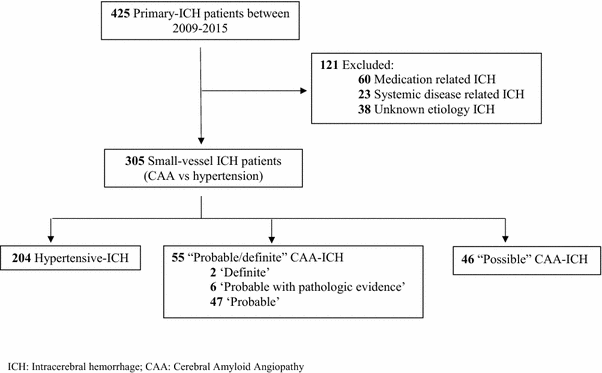 Primary Intracerebral Hemorrhage A Closer Look At Hypertension And
Primary Intracerebral Hemorrhage A Closer Look At Hypertension And
The varied clinical presentation of ich ranging from minor.
Hemorrhagic stroke pathophysiology diagram. Pathophysiology of haemorrhagic stroke. The primary pathophysiology of stoke is an underlying heart or blood vessel disease. Stroke is one of the leading causes of death globally and in canada.
There are two types of hemorrhagic stroke called intracerebal and subarachnoid. There are two major classifications of stroke. Two types of weakened blood vessels usually cause hemorrhagic stroke.
The clot resolves sporadically. The two types of hemorrhagic strokes are intracerebral within the brain hemorrhage or subarachnoid hemorrhage. Pathophysiology of ischemic stroke.
Intracerebral hemorrhage ich is a devastating form of cerebrovascular disorder with a high mortality and morbidity. Intracerebral hemorrhage ich is an often fatal type of stroke that kills 30 000 people annually in the united states. Pathophysiology of hemorrhagic stroke the main type of hemorrhage that can lead to stroke is subarachnoid hemorrhage.
A hemorrhagic stroke is either a brain aneurysm burst or a weakened blood vessel leak. The ultimate result of ischemic cascade initiated by acute stroke is neuronal death along with an irreversible loss of neuronal function. A tia is similar to a stroke but the interruption of blood flow is temporary.
In addition the pressure may lead to a loss of blood supply to affected tissue with resulting infarction. The pathophysiology of stroke is complex and involves excitotoxicity mechanisms inflammatory pathways oxidative damage ionic imbalances apoptosis angiogenesis and neuroprotection. Blood spills into or around the brain and creates swelling and pressure damaging cells and tissue in the brain.
Aneurysms and arteriovenous malformations avms. In this type of bleed which usually results from head trauma or a ruptured aneurysm there is uncontrolled bleeding between the innermost two of the three meninges membranes lining the brain. A hemorrhagic stroke occurs when a weakened blood vessel ruptures.
Haemorrhagic strokes are due to the rupture of a blood vessels leading to compression of brain tissue from an expanding haematoma. Pathophysiology of hemorrhagic stroke springerlink. If the patient survives the ictus then the resulting hematoma within brain parenchyma triggers a series of adverse events causing secondary insults and severe neurological deficits.
Intracerebral hemorrhage ich a subtype of hemorrhagic stroke is as sociated with substantial morbidity and mortality. This can distort and injure tissue. Clinical studies have recently risen to improve outcome for patients with.
 Pathophysiologic Features Of Intracerebral Hemorrhage Adapted From
Pathophysiologic Features Of Intracerebral Hemorrhage Adapted From
Cerebral Palsy Mcmaster Pathophysiology Review
 Schematic Diagram Illustrating The Main Contributory Factors
Schematic Diagram Illustrating The Main Contributory Factors
 Long Term Recurrent Subarachnoid Hemorrhage After Adequate Coiling
Long Term Recurrent Subarachnoid Hemorrhage After Adequate Coiling
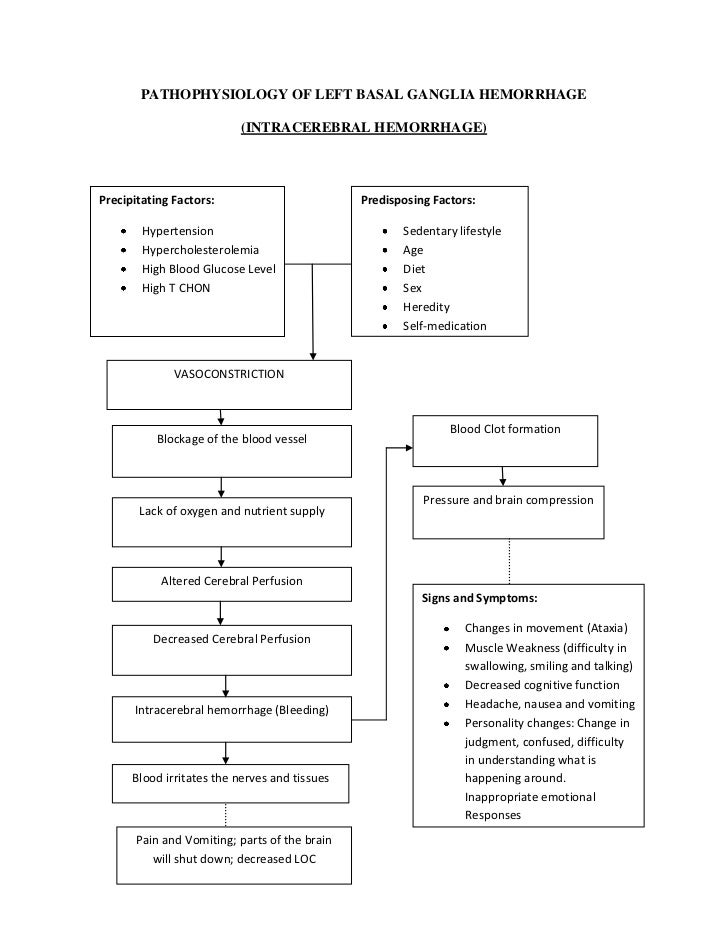
 Pathophysiology Of Left Basal Ganglia Hemorrhage
Pathophysiology Of Left Basal Ganglia Hemorrhage
Herpes Zoster And The Risk Of Ischemic And Hemorrhagic Stroke A
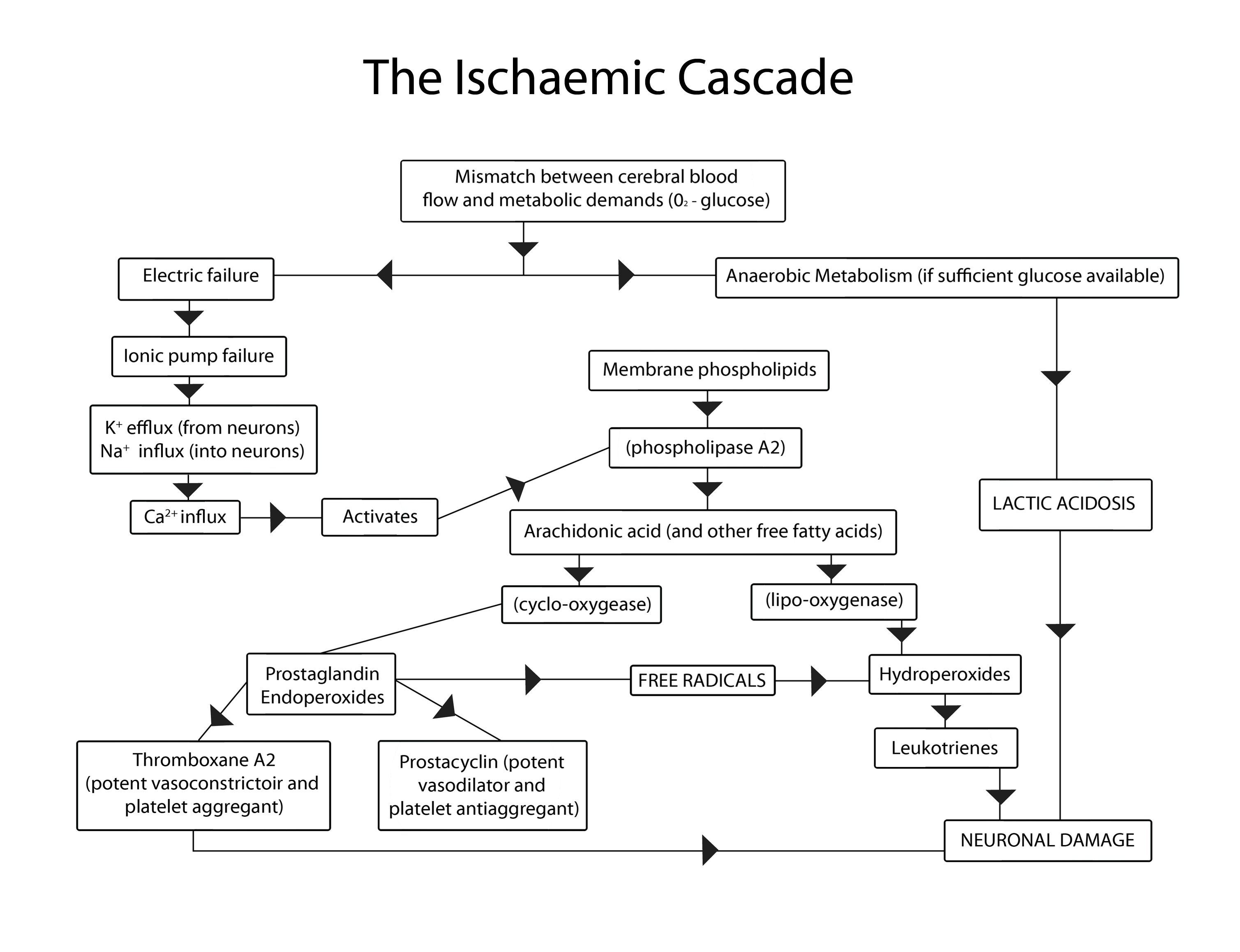 Pathophysiology Neuro4students
Pathophysiology Neuro4students
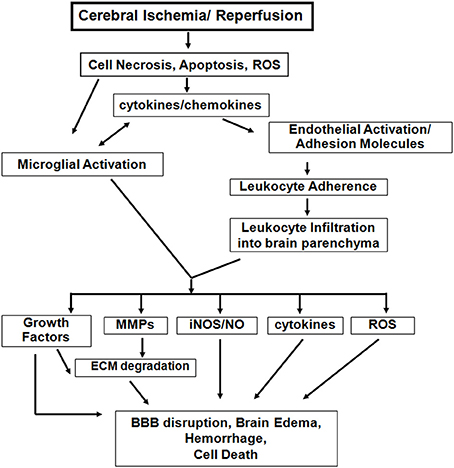
 Role Of Neuroinflammation In Ischemic Stroke
Role Of Neuroinflammation In Ischemic Stroke
 Stroke Prevention By Direct Revascularization For Patients With
Stroke Prevention By Direct Revascularization For Patients With
 Frontiers Barrier Mechanisms In Neonatal Stroke Neuroscience
Frontiers Barrier Mechanisms In Neonatal Stroke Neuroscience
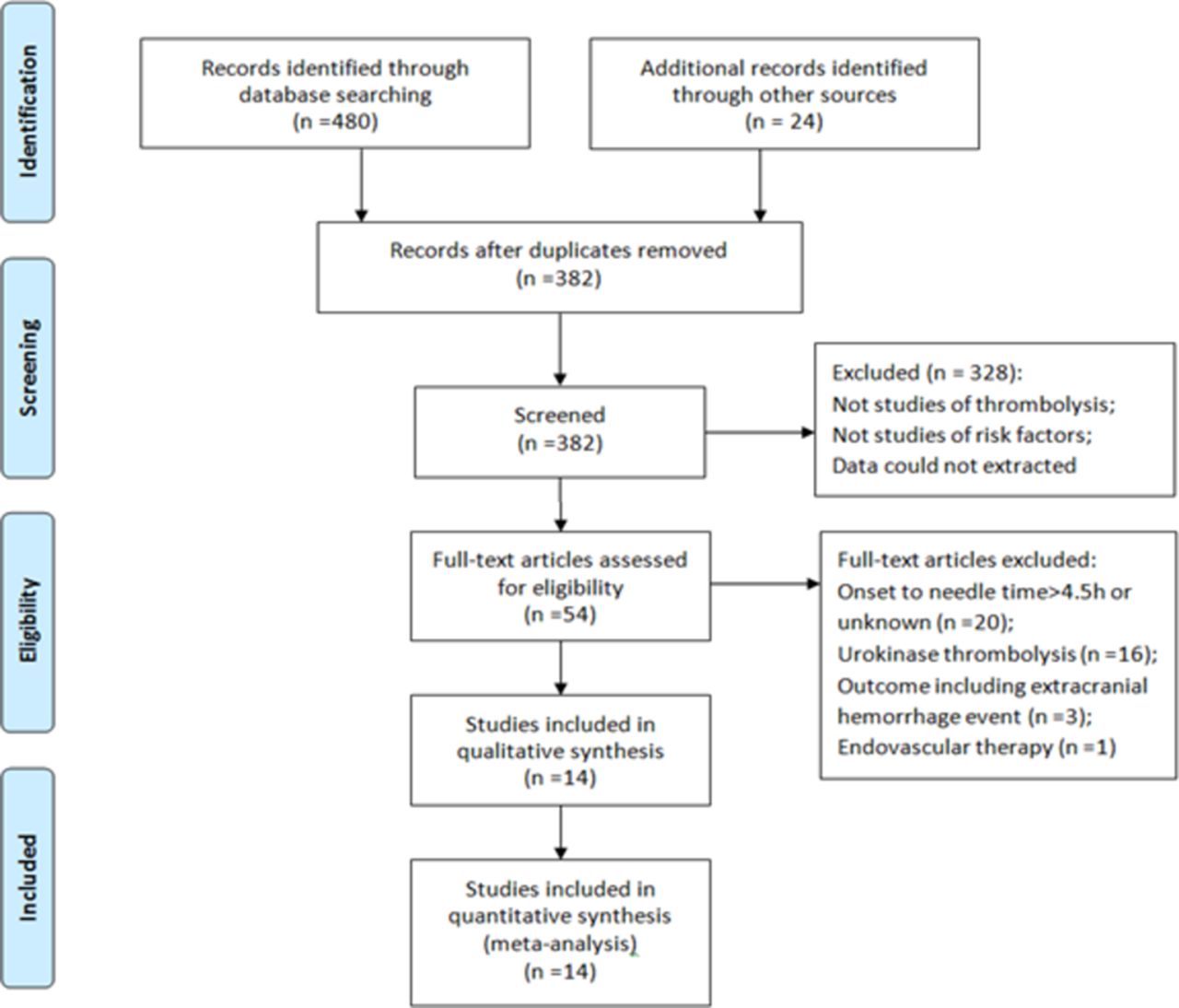 Risk Factors Of Haemorrhagic Transformation For Acute Ischaemic
Risk Factors Of Haemorrhagic Transformation For Acute Ischaemic
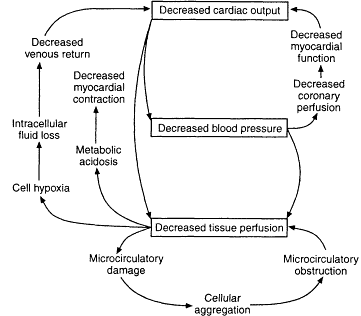 2 Pathophysiology Of Acute Hemorrhagic Shock Fluid Resuscitation
2 Pathophysiology Of Acute Hemorrhagic Shock Fluid Resuscitation
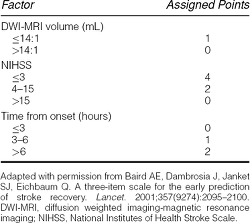 Ce Acute Stroke Pathophysiology Diagnosis And Treatment
Ce Acute Stroke Pathophysiology Diagnosis And Treatment
 Fever After Subarachnoid Hemorrhage Neurology
Fever After Subarachnoid Hemorrhage Neurology
 Hemorrhagic Stroke National Stroke Association
Hemorrhagic Stroke National Stroke Association
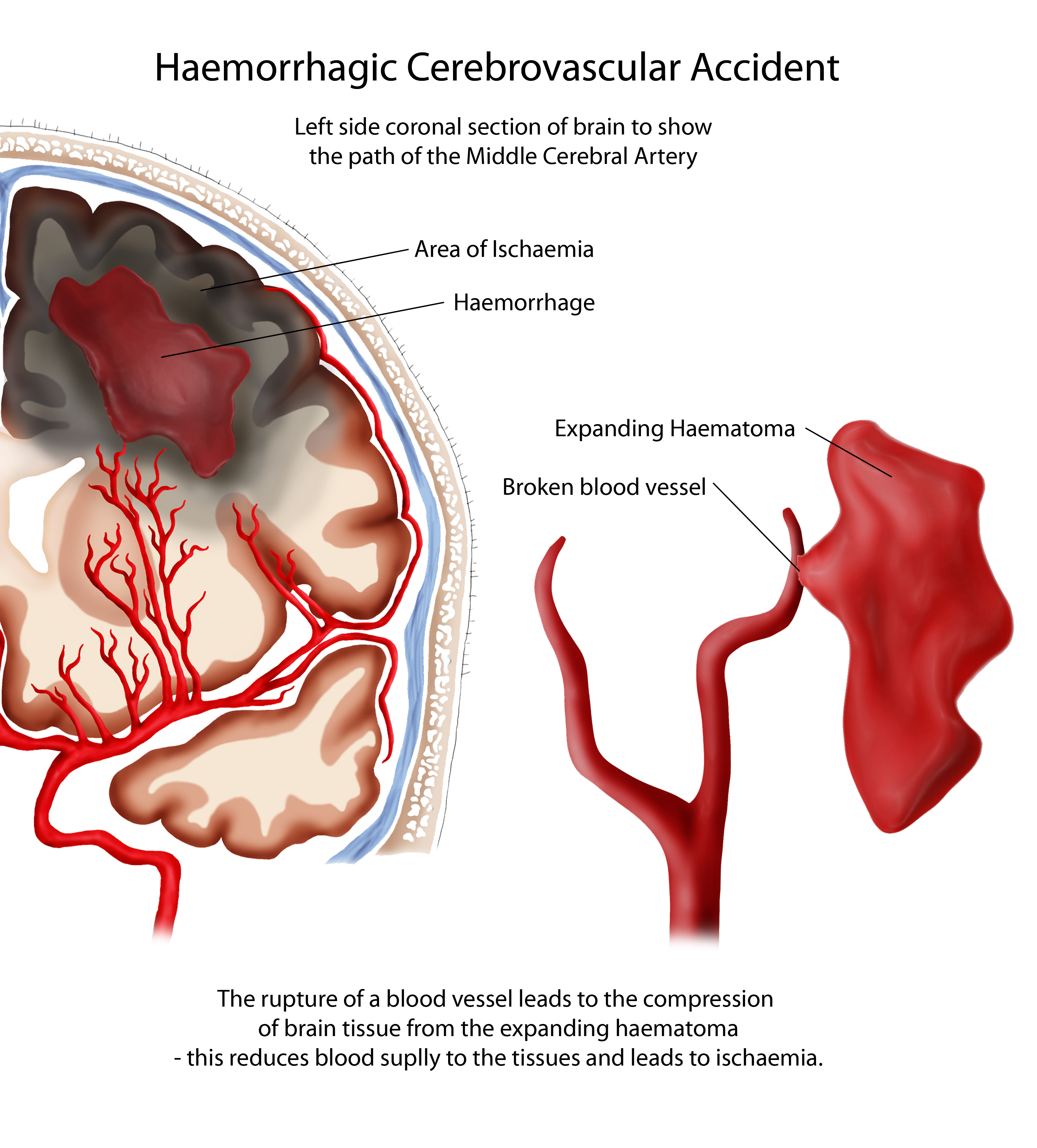 Pathophysiology Neuro4students
Pathophysiology Neuro4students
Effect Of A 72 Hour Stroke Care Bundle On Early Outcomes After Acute
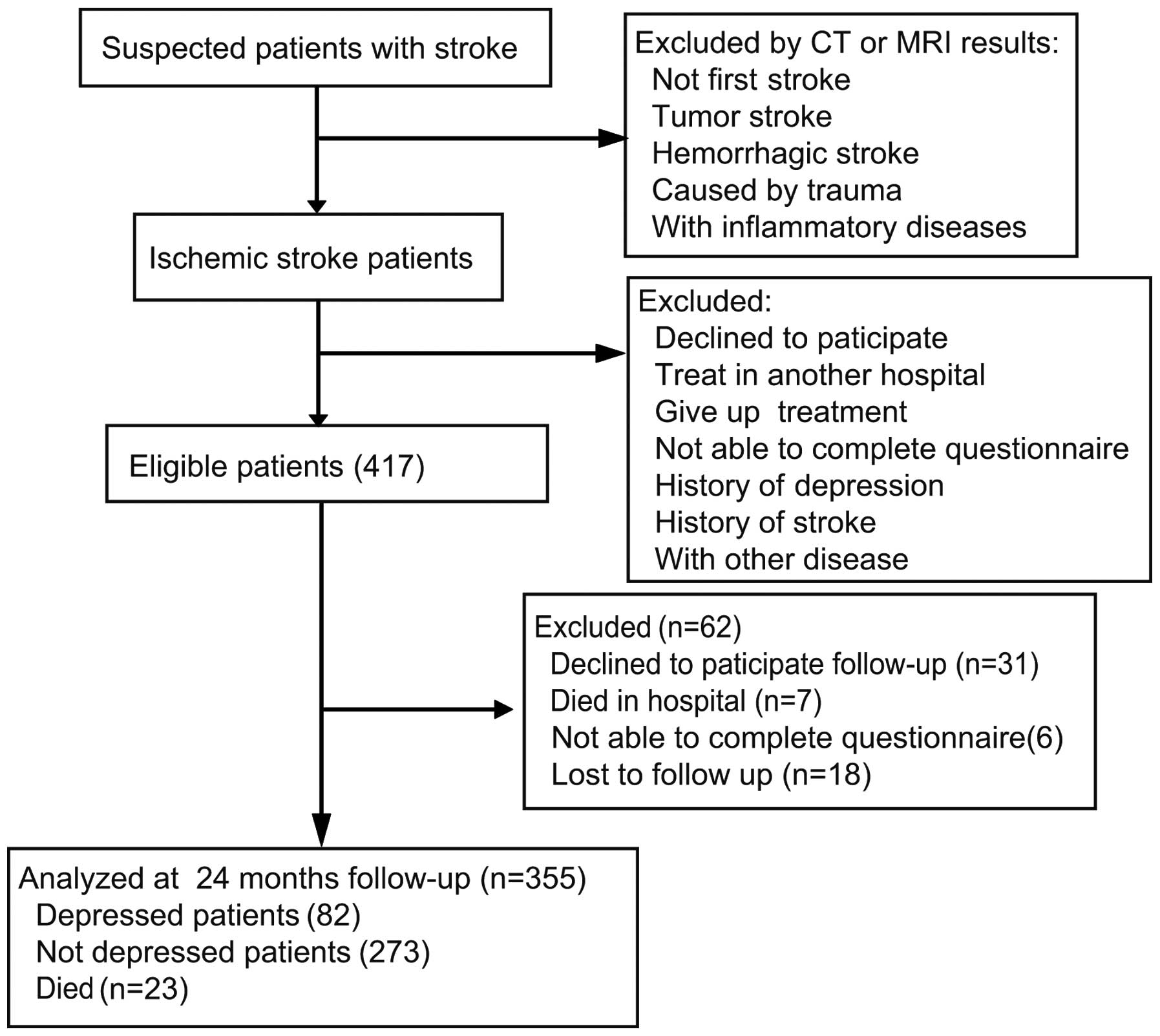 Association Between Inflammatory Cytokines And The Risk Of Post
Association Between Inflammatory Cytokines And The Risk Of Post
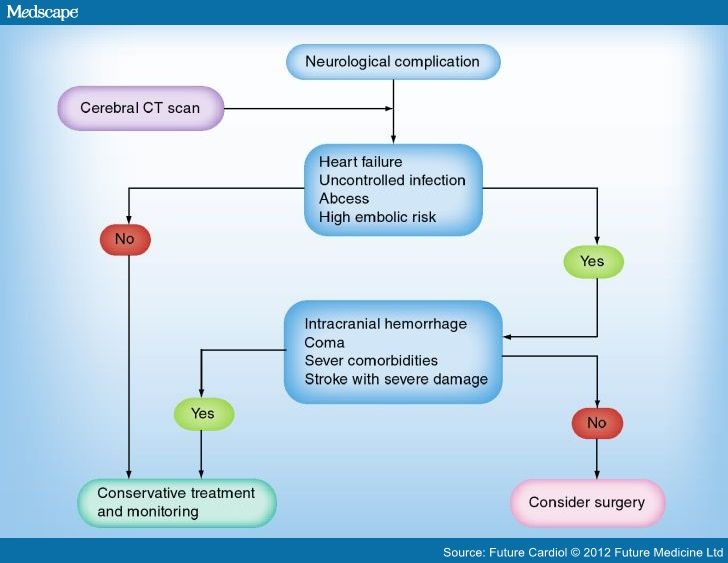 Treatment Options For Patients With Infective Endocarditis
Treatment Options For Patients With Infective Endocarditis
 Overview Of Hemorrhagic Stroke Brain Spinal Cord And Nerve
Overview Of Hemorrhagic Stroke Brain Spinal Cord And Nerve
 Figure 1 From Anticoagulation In Acute Ischemic Stroke A Systematic
Figure 1 From Anticoagulation In Acute Ischemic Stroke A Systematic

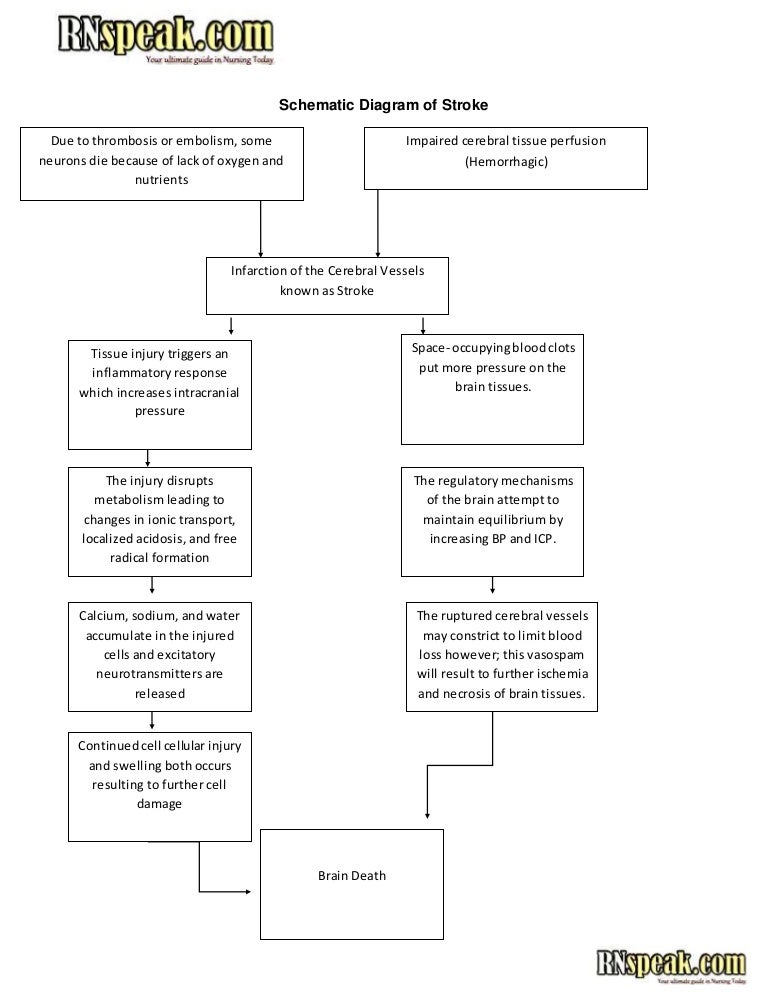
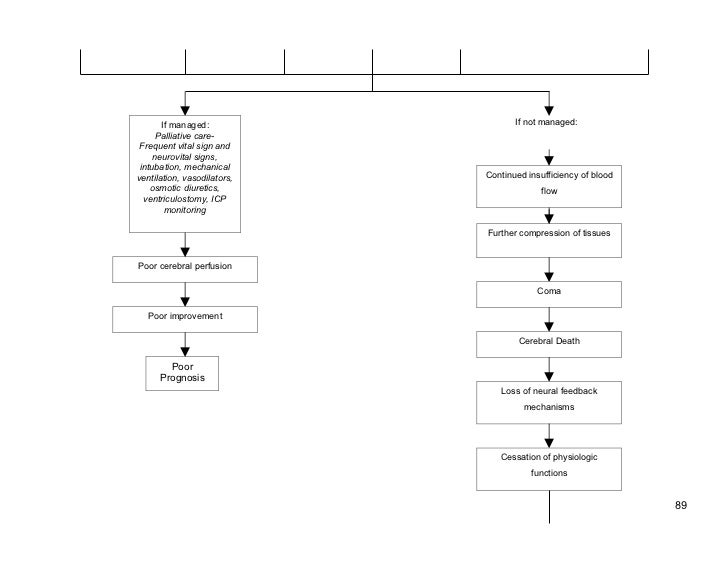


0 Response to "Hemorrhagic Stroke Pathophysiology Diagram"
Post a Comment